Manage Bulging & Herniated Disc Pain With Spinal Decompression
Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression. Effective and safe pain treatment.
Video Transcript
Do you suffer from back pain, neck pain or sciatica? If you do, you'll be glad to hear that we offer safe and effective spinal decompression therapy in our office.
Non-surgical spinal decompression is a great way to restore your back to health. Studies have shown that spinal decompression can effectively treat back pain, sciatica, disk herniations, and other pain conditions.
How does spinal decompression help your spine heal? Your spine is made up of bones called vertebrae, and these are separated by tough, fibrous, flexible disks. The disks allow your spine to flex, bend, and twist - and also act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae.
If your back is injured, strained, or if you have chronic pain, the individual segments of your spine can become immobile, tight, and restricted. This fixation of the spine creates tremendous pressure on the disks.
This pressure can cause the disks to bulge or herniate, or can cause inflammation in the nerves that travel from your spinal cord to the rest of your body. If the nerves become irritated or pinched, it can cause back pain, sciatica, or even numbness and tingling in your hip and leg.
Spinal decompression works by gently stretching your spine and reducing the pressure on your disks, restoring your spine's natural function and flexibility.
The treatment process is easy and relaxing. First, the doctor will determine the specific area of the spine to target, and configure the decompression machine. During a decompression treatment, you will lie comfortably on a padded table. A belt fits around your waist and your lower chest.
Then, the computer-controlled decompression system slowly and precisely stretches your spine, then releases. Over the course of a treatment, your spine will be carefully stretched and relaxed many times, “decompressing” the affected disks of the spine. This increases circulation, hydration, and nutrition to the disk.
Medical studies have shown the effectiveness of spinal decompression. In 2010, researchers performed CT scans on patients before and after spinal decompression and found that not only did they have a dramatic improvement in symptoms, but there was also a significant improvement in disk height after treatment.
A 1998 study found that spinal decompression patients had a 90% reduction in disk herniations measured by MRI scans.
And, a 2008 Stanford University study found that non-surgical decompression resulted in an 83% reduction in back pain, with a high rate of patient satisfaction.
Medical Studies in 2017, demonstrate that Non-Surgical Decompression improves the actual disc herniation.
CONCLUSIONS: This study showed that patients with herniated discs and who received decompression therapy had improvement based on clinical and radiologic evidence. Non-Surgical Decompression Therapy can be used in treatment of lumbar disc herniation and has been shown to reduce the size of and symptoms associated with the herniation.
Demirel, A., Yorubulut, M. and Ergun, N., 2017. Regression of lumbar disc herniation by physiotherapy. Does non-surgical spinal decompression therapy make a difference? Double-blind randomized controlled trial. Journal of back and musculoskeletal rehabilitation, 30(5), pp.1015-1022.
You don't need to suffer from back pain, neck pain, or sciatica! Call our office today to see if non-surgical spinal decompression therapy can help you get back to health!
Spinal Disc Conditions
Disc Bulge: Definition
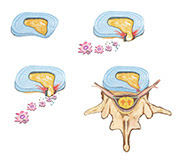
A disc bulge occurs when the tough outer fibers of the spinal disc weaken and stretch allowing the jellylike center of the disc to expand “bulge” outward in all directions (360 degrees). A disc bulge is another term for disc degeneration and can cause pain directly from the disc or by compressing other structures containing nerves.
Herniated Disc: Definition
A herniated disc occurs when an event occurs that exerts traumatic forces into the disc forcing the jellylike center outward through the tough cartilage fibers. The displacement of center causes tearing in the cartilage fibers which can cause pain as well as possible compression of important tissues like the spinal cord or spinal nerves. The events that cause a herniated disc include car crashes, sports injuries and slip and falls.
Disc Bulge / Disc Herniation: Symptoms
The majority of symptoms caused by a Disc Bulge or Herniated Disc are related to irritation of spinal nerves. These nerves exit the spine through small holes called foramen. The spinal discs are located next to these nerve passageways, and the bulging of the disc material can “pinch” these nerves, thereby creating a variety of uncomfortable and sometimes debilitating symptoms.
Disc Bulge / Herniated Disc of the Low Back: Lumbar Spine Disc Bulge
A Disc Bulge in the low back can cause low back pain or numbness, tingling, burning, sharp pain or weakness in the legs or feet. Sharp pain in the back of the legs is often referred to as Sciatica.
Disc Bulge / Herniated Disc of the Neck: Cervical Spine Disc Bulge
A Disc Bulge in the neck can cause neck pain, or in more severe cases, numbness, tingling, burning, sharp pain or weakness in the arms or hands.
Treatment: Using Hill DT Non-Surgical Spinal Disc Decompression
Thoracic Disc Herniation
Due to the limited motion in the thoracic spine caused by the bony barrier of the ribs, thoracic disc herniations are relatively rare. However, when they do occur, they can create much pain and dysfunction.
The surgical access to the thoracic disc is more complicated than other parts of the spine and may involve the removal of a rib to access an injured disc. This is a complicated surgery that can lead to other unintended consequences. Whenever practical and safe, conservative (nonsurgical) care, such as chiropractic, is advisable prior to the use of more invasive procedures, such as spinal injections or surgery.